

- Virtualbox vs vmware vs hyper v windows 10#
- Virtualbox vs vmware vs hyper v software#
- Virtualbox vs vmware vs hyper v windows#

This makes it a perfect tool for end-user productivity. VirtualBox, in contrast, is a type 2 hypervisor and can allow users to have quick access to the alternative guest OS alongside the primary host’s operating system. Hyper-V provides high-performance VMs since it is a type 1 hypervisor and can access the physical hardware directly, without necessarily loading the underlying hardware’s OS. Hyper-V and VirtualBox can both serve as a basis for server virtualization in small to mid-sized businesses (SMBs), but they also have distinct performances that set them apart. However, although Hyper-V also integrates seamlessly with Windows-based infrastructures, it isn’t as simple to set up as VirtualBox. You can also achieve the same user experience with VirtualBox, which provides a VM creation wizard. Once activated, you can begin creating VMs via its Quick Create VM creation option or use a more advanced process through the Hyper-V Manager.
Virtualbox vs vmware vs hyper v windows#
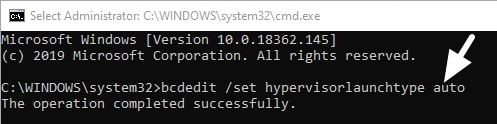
To start using Hyper-V, you must enable it through the PowerShell or Windows features.
Virtualbox vs vmware vs hyper v windows 10#
However, the company doesn’t provide this feature with Windows 10 or Windows 11 Home editions. Microsoft has integrated Hyper-V with Windows 10 and Windows 11 for Pro, Education, and Enterprise editions. Unlike Hyper-V, which takes control of the BIOS or UEFI automatically when the computer starts, users can start or stop VirtualBox manually on demand. They support guest VMs by coordinating calls for the CPU, memory, and storage resources through the underlying physical host’s OS. A type 2 hypervisor-also called a hosted hypervisor-runs on top of an OS, unlike type 1 hypervisors that usually execute on the underlying physical hardware. VMs can then be initiated manually by users or automatically, depending on the Hyper-V’s settings. When a physical host starts, usually a Hyper-V takes control from the basic input-output system (BIOS) or unified extensible firmware interface (UEFI) and initiates the management OS. Hyper-V is a classic example of a type 1 hypervisor.
For this reason, type 1 hypervisors usually take the place of the host OS. A type 1 hypervisor runs directly on the underlying physical hardware, interacting directly with the processor, RAM, and storage. There are two basic categories of hypervisors: The guest VMs effectively share the physical host’s computing resources, such as the processor cycles, RAM, network bandwidth, and storage. It decouples the OSs and applications from the underlying physical server, enabling it to run multiple virtual machines (VMs) as guests.
Virtualbox vs vmware vs hyper v software#
Hypervisors: Differences between Hyper-V and VirtualBoxĪ hypervisor is a crucial software that makes virtualization possible. VirtualBox and why Parallels® RAS is another alternative-so you can make an informed choice. In this post, we’ll explore the differences between Hyper-V vs. There are several virtualization options provided by various vendors for Windows users, each with its own functionality, ease-of-use, and performance capabilities. It’s a fundamental tool in the virtualization world that powers the “anything-as-a-service” models in cloud computing. A hypervisor allows multiple operating systems (OSs) and applications to run on the same physical host, allowing organizations to consolidate IT resources, lower costs, and increase efficiency.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
